FAQs
Cyanoacrylates – also known as instant adhesives, CA glue, superglue, and Krazy Glue – are high-strength, quick-bonding glues that are widely applicable across industries, from automotive components and medical devices to guitar fabrication. On this page, the Aron Alpha team has covered some of the most common questions we’ve received regarding cyanoacrylates.
We’ll provide answers regarding how long cyanoacrylate takes to cure, cyanoacrylate glue temperature range, and cyanoacrylate viscosity, among other aspects.
What Is Cyanoacrylate Made Of?
So, what is cyanoacrylate made of, exactly? Cyanoacrylate glue consists of a type of acrylic resin called cyanoacrylate, which provides near-instant curing when it reacts with water’s hydroxyl ions. Once cured, the cyanoacrylate transforms to a plastic state, creating a strong, reliable bond between surfaces.
How Do Temperature and Humidity Impact Cyanoacrylate Adhesives?
It’s important to keep in mind the cyanoacrylate glue temperature range and how it affects the adhesive’s performance. The curing speed of cyanoacrylate adhesives will increase with temperature. A common rule of thumb is that for every 10°C increase in temperature, the reaction rate roughly doubles. Conversely, lowering the temperature by 10°C can slow the curing process. For example, a cyanoacrylate adhesive that cures in 5 seconds at 30°C might take closer to 10 seconds to cure at 20°C, depending on the substrate and moisture levels.
In addition to temperature, humidity also affects the cure time of cyanoacrylate adhesives. Because these adhesives cure in the presence of moisture, lower humidity can slow down cure times, whereas higher humidity generally speeds up curing. This means that curing times can vary widely in environments with fluctuating temperatures and humidity levels.
How Long Does Cyanoacrylate Take to Cure?
Cyanoacrylate adhesives offer faster cure times than other types of adhesives due to their fast reaction rate. However, certain factors will influence how long the adhesive takes to cure. Typically, the average fixture time for cyanoacrylate is around 5 to 90 seconds, while full curing requires around 8 to 24 hours.
The specific amount of time it takes for cyanoacrylate adhesives to cure depends on the types of surfaces involved and their moisture absorption capabilities. It also depends on the specific type of cyanoacrylate, such as surface-insensitive and hybrid types. The former offers almost instant cure times, while hybrid epoxies tend to take longer to cure.
What Materials Are and Are Not Compatible With Cyanoacrylate Adhesives?
Cyanoacrylate glues bond readily with a wide variety of materials, including metal, fiber composite, plastic, vinyl, silicone, and rubber. Some plastics such as PTFE, polypropylene, and polyethylene are more difficult to bond using cyanoacrylates; however, Aron Alpha’s products can be specially engineered to meet the particular needs of your application.
When deciding whether to use Krazy Glue or other cyanoacrylate adhesives for your project, it is important to consider factors that could compromise your super glue’s bonding ability, including lack of moisture, substrate acidity, and material formulations that make it difficult for cyanoacrylates to bond, such as polyolefin, acetal, and fluoropolymers.
For low surface energy plastics such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or any polyolefin plastic, a surface treatment primer will most likely be required to achieve high bond strength with cyanoacrylate adhesives. See section on Primers.
What Are Common Applications for Cyanoacrylate Adhesives?
Aron Alpha adhesive products are relied upon by engineers in a variety of industries for dependable assembly and process bonding. Applications that benefit from the implementation of cyanoacrylate adhesives include:
- Automotive components and subassemblies
- Aerospace parts and assemblies
- Musical instruments
- Commercial and residential appliance components
- Furniture, home electronics, and other consumer goods
- Disposable medical equipment and devices
Industries such as automotive, electronics, and general assembly use cyanoacrylate adhesives to ensure a quick, efficient, and dependable bond at a low overall cost. Krazy Glue and other cyanoacrylate adhesives provide durable bonds in situations where traditional fasteners are complicated to install or take up too much space.
What is the Best Way to Store Cyanoacrylate Adhesives?
To ensure optimal super glue shelf life, we recommend storing your unopened bottles of instant adhesives in a cool, dry location, with sustained temperatures between 35°F and 45°F. Be sure that your adhesive container is not exposed to the elements, as wide temperature fluctuations and exposure to moisture and sunlight can damage the outer container and the adhesive within.
Before opening your cyanoacrylate adhesive, allow it to warm to room temperature. If you do not use it all at once, store it at room temperature and keep in mind that the product’s shelf life is reduced once opened. Avoid refrigerating your adhesive after opening, as this can cause moisture to collect inside the package, which reduces the quality and shelf life of your Aron Alpha product.
How Should I Use Accelerators and Primers with Cyanoacrylate Adhesives?
Solvent-based adhesive accelerators and primers are used to enhance the curing speed of cyanoacrylates, ultimately making them even more practical. Also known as adhesive activators, accelerators can be added to the adhesive prior to or after application, depending on the design configuration and bonding needs of the material. Although they can be particularly useful for facilitating speedy curing in cold, dry conditions, it is important for us to disclose that accelerators can reduce the bond strength of cyanoacrylate adhesives, which is particularly risky for porous materials, as an accelerant can cause the glue to cure before it is sufficiently absorbed.
Here is a blog we put together that talks more in-depth about accelerators and primers.
How Can I Remove Cyanoacrylate Adhesives?
The great strength of cyanoacrylate adhesives is also one of their most notable challenges. The strong bonding properties of Krazy Glue make it equally likely to bond to unwanted materials, such as your skin and clothing. Fortunately, if you know how to remove cyanoacrylate adhesives using certain solvents, you can prevent undesirable bonds and remove any residual adhesive on your finished surfaces.
Certain solvents can be used to remove cyanoacrylate adhesives from skin, fabric, glass, metal, plastic, vinyl, and more. The type of solvent you need depends largely on the material you are trying to remove the adhesive from. Certain areas of the skin may be sensitive to acetone; however, it is an ideal solvent for use on fabric, metal, glass, plastic, and non-sensitive skin. Other remedies, such as peanut butter or vegetable oil, are ideal for use on sensitive skin, fragile plastics, and vinyl. In some cases, you can opt to use physical force to remove superglue with a hammer, paint scraper, or razor blade.
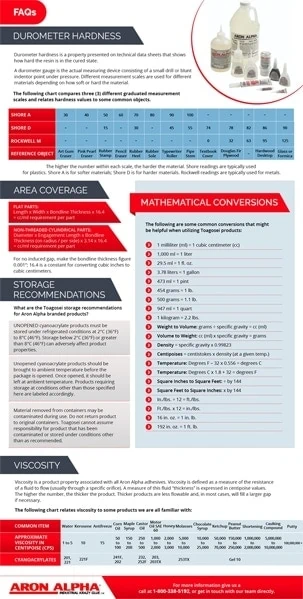
Durometer Hardness
Durometer hardness is a property presented on technical data sheets that shows how hard the resin is in the cured state.
A durometer gauge is the actual measuring device consisting of a small drill or blunt indentor point under pressure. Different measurement scales are used for different materials, depending on how soft or hard the material is.
The following chart compares three (3) different graduated measurement scales and relates hardness values to some common objects.
| Shore A | Shore D | Rockwell M | Reference Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | – | – | Art Gum Eraser |
| 40 | – | – | Pink Pearl Eraser |
| 50 | 15 | – | Rubber Stamp |
| 60 | – | – | Pencil Eraser |
| 70 | 30 | – | Rubber Heel |
| 80 | – | – | Rubber Sole |
| 90 | 45 | – | Typewriter Roller |
| 100 | 55 | – | Pipe Stem |
| – | 74 | 0 | Textbook Cover |
| – | 78 | 32 | Douglas Fir Plywood |
| – | 82 | 63 | – |
| – | 86 | 95 | Hardwood Desktop |
| – | 90 | 125 | Glass or Formica |
The higher the number within each scale, the harder the material. Shore readings are typically used for plastics. Shore A is for softer materials; Shore D is for harder materials. Rockwell readings are typically used for metals.
Mathematical Conversions
The following are some common conversions that might be helpful when utilizing Toagosei products:
- 1 milliliter (ml) = 1 cubic centimeter (cc)
- 1,000 ml = 1 liter
- 29.5 ml = 1 fl. oz.
- 3.78 liters = 1 gallon
- 473 ml = 1 pint
- 454 grams = 1 lb.
- 500 grams = 1.1 lb.
- 947 ml = 1 quart
- 1 kilogram = 2.2 lbs.
- Weight to Volume: grams ÷ specific gravity = cc (ml)
- Volume to Weight: cc (ml) x specific gravity = grams
- Density = specific gravity x 0.99823
- Centipoises = centistokes x density (at a given temp.)
- Temperature: Degrees F – 32 x 0.556 = degrees C
- Temperature: Degrees C x 1.8 + 32 = degrees F
- Square Inches to Square Feet: ÷ by 144
- Square Feet to Square Inches: x by 144
- In./lbs. ÷ 12 = ft./lbs.
- Ft./lbs. x 12 = in./lbs.
- 16 in. oz. = 1 in. lb.
- 192 in. oz. = 1 ft. lb.
Area Coverage
Flat Parts:
Length x Width x Bondline Thickness x 16.4 = cc/ml requirement per part
Non-threaded Cylindrical Parts:
Diameter x Engagement Length x Bondline Thickness (on radius / per side) x 3.14 x 16.4 = cc/ml requirement per part
For no induced gap, make the bondline thickness figure 0.001″; 16.4 is a constant for converting cubic inches to cubic centimeters.
Shelf Life
What is the Toagosei shelf life policy for Aron Alpha branded products?
UNOPENED cyanoacrylate products must be stored under refrigerated conditions at 1°C (34°F) to 5°C (40°F). Storage below 1°C (34°F) or greater than 5°C (40°F) can adversely affect product properties.
Unopened cyanoacrylate products should be brought to ambient temperature before the package is opened. Once opened, it should be left at ambient temperature. Products requiring storage at conditions other than those specified here are labeled accordingly.
Material removed from containers may be contaminated during use. Do not return product to original containers. Toagosei cannot assume responsibility for product that has been contaminated or stored under conditions other than as recommended.
Contact Customer Service at 614-718-3855 or 1-800-338-5192 if you need additional information.
Cyanoacrylate Viscosity
Cyanoacrylate viscosity is a product property associated with all Aron Alpha adhesives. Viscosity is defined as a measure of the resistance of a fluid to flow (usually through a specific orifice). A measure of this fluid “thickness” is expressed in centipoise values. The higher the number, the thicker the product. Thicker products are less flowable and, in most cases, will fill a larger gap if necessary.
The following chart relates cyanoacrylate viscosity to some products we are all familiar with:
| Common Item | Approximate Viscosity in Centipoise (cps) | Cyanoacrylates |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 1 to 5 | 201, 221 |
| Kerosene | 10 | 221F |
| Antifreeze | 15 | |
| Corn Oil | 50 to 100 | 241F, 202 |
| Maple Syrup | 150 to 200 | |
| Castor Oil | 250 to 500 | 232, 252F |
| Motor Oil SAE 60 | 1,000 to 2,000 | 203, 203TX |
| Honey | 2,000 to 3,000 | |
| Molasses | 5,000 to 10,000 | 253TX |
| Chocolate Syrup | 10,000 to 25,000 | |
| Ketchup | 50,000 to 70,000 | |
| Peanut Butter | 150,000 to 250,000 | Gel 10 |
| Shortening | 1,000,000 to 2,000,000 | |
| Caulking Compound | 5,000,000 to 10,000,000 | |
| Putty | 100,000,000 + |
Cyanoacrylates at Aron Alpha
Toagosei America Inc. has been manufacturing the Aron Alpha brand of cyanoacrylate instant adhesives for over 50 years. As an ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015-certified company, we can provide quality, high-performance solutions for a range of substrates and application requirements.
For more information about the benefits and uses of Aron Alpha’s cyanoacrylate adhesive products, view our blog, “How Cyanoacrylate Adhesives Work and Their Industrial Applications”.
Have a question about cyanoacrylates that we didn’t answer here? Feel free to reach out to our team today, and we’ll provide more information.